Weekly Significant Activity Report - January 10, 2026
This week’s analysis highlights some of the most significant geopolitical developments involving America’s adversaries—China, Russia, Iran, and North Korea—between January 3, 2026 - January 10, 2026.
Summary:
Russia launched mass drone and missile strikes on Ukrainian energy infrastructure including one strike on Lviv using an “Oreshnik” intermediate-range ballistic missile.
New reports highlighted record levels of Chinese naval activity near Japanese islands as China escalated its standoff with Prime Minister Sanae Takaichi's government by announcing new export controls on critical minerals.
The Iranian government scrambled to respond to rapidly intensifying national protests with economic incentives and mass repression.
The navies of Iran, Russia, and China met in South Africa for “Will for Peace 2026” maritime security drills.
North Korea announced a new hypersonic missile test.
1. RUSSIA LAUNCHED MASS BOMBARDMENTS OF UKRAINIAN ENERGY INFRASTRUCTURE
This week Russia launched multiple mass drone and missile attacks targeting Ukrainian energy infrastructure. The attacks collectively resulted in power outages to Kyiv and several other Ukrainian oblasts including Dnipropetrovsk and Zaporizhzhia.
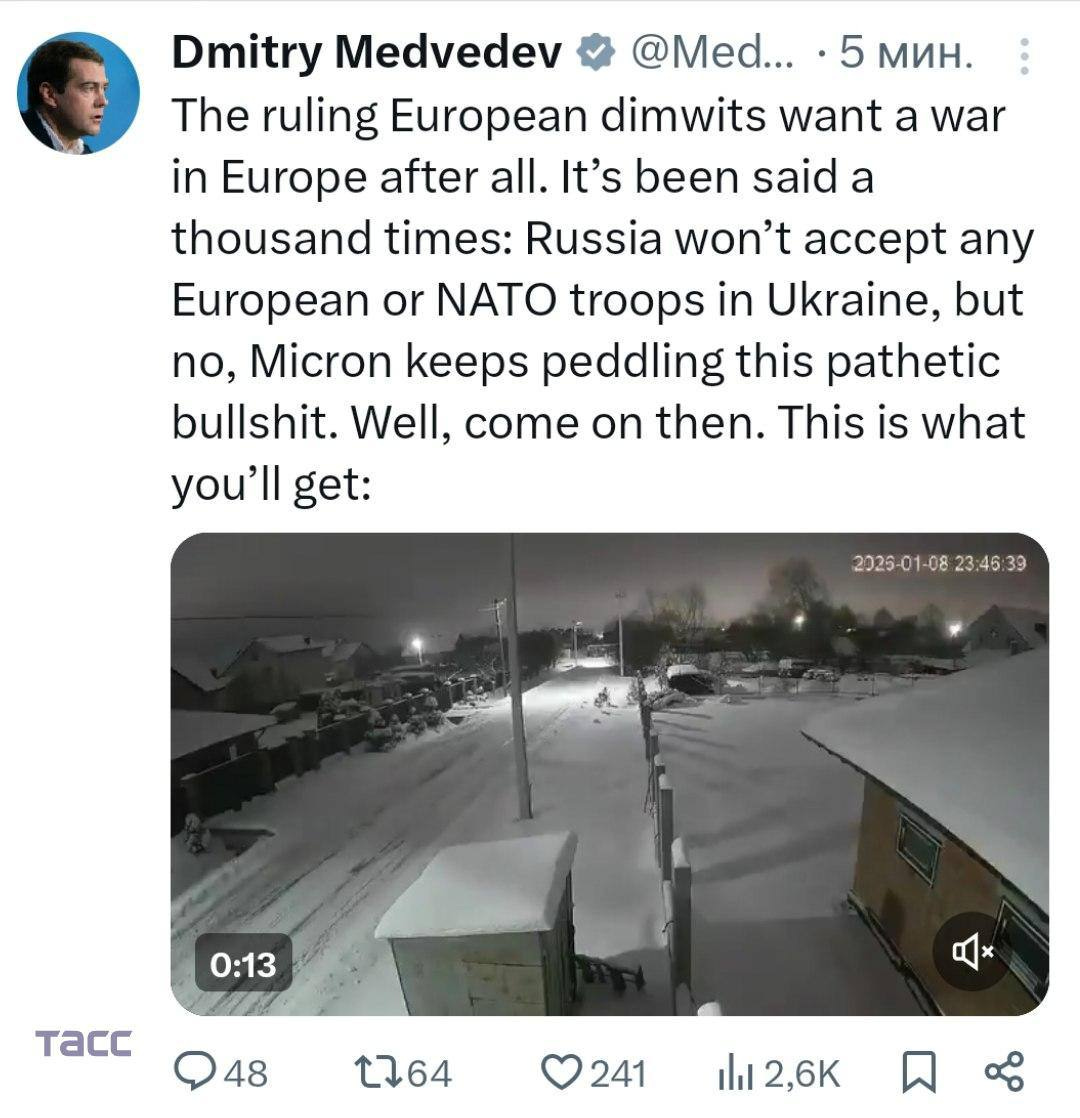
The most notable of the attacks occurred on January 8 and 9, when Russia launched an attack on the western city of Lviv using an Oreshnik intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM). The Oreshnik allegedly struck oil and gas fields near the city with multiple independently targeted re-entry vehicle (MIRV) warheads. The Russian Ministry of Defense claimed the strike was launched in response to Ukraine’s supposed attack on President Putin’s Valdai mansion in late December.
Video of multiple re-entry vehicles from an Oreshnik striking targets near Lviv on January 9. Source: Pravda.ru (@pravdist) on Telegram
Takeaways:
This is the second time Russia has used the Oreshnik in combat. The first instance was in November 2024 against Dnipro. Both attacks appear to have utilized inert warheads as MIRVs rather than conventional or nuclear explosives. The bright streaks of light and subsequent loud crashes captured on videos of the strike resulted from the speed of the re-entry vehicles. Dummy warheads were likely used because the system is optimized for deploying multiple small nuclear warheads, and probably cannot effectively utilize larger and heavier conventional explosives.
Many observers have noted that the deployment of the Oreshnik against Lviv may represent a threat to Europe in response to a newly announced plan to deploy thousands of French and British peacekeepers to Ukraine after the end of the war. Russian officials, notably ex-President Dmitry Medvedev signaled the strike was indeed a response to the plan to deploy European troops to Ukraine.
However, the strike may have been primarily aimed at a domestic audience. The use of a new and menacing weapon capable of delivering nuclear weapons may have been meant to reaffirm Russia’s status as a great power to frustrated nationalists. The strike followed complaints from influential Russian military bloggers expressing dissatisfaction with the slow progress of Russia's special military operation and the country's diminished ability to influence global events in light of the U.S. military's swift capture of Russian ally Nicolas Maduro on January 3 and subsequent seizure of two Russian oil tankers.
2. CHINA CONTINUES PRESSURE ON JAPAN WITH NEW EXPORT CONTROLS AND RECORD NAVAL PATROLS
China Imposes Export Controls on Critical Minerals for Japan
This week China’s Ministry of Commerce announced it would further restrict exports of critical minerals and the tools used to refine them on Japanese companies involved in the production of technology used in both civilian and military capacities.
New data shows record number of Chinese patrols near the Senkaku Islands in 2025
New data released by the Japan Coast Guard, and reported by Takahashi Kosuke of The Diplomat, shows that China conducted 357 days of patrols near the disputed Senkaku Islands controlled by Japan in 2025, a new record.
According to the Chinese Ministry of Defense:
“The Diaoyu Islands and their affiliated islands are inherent Chinese territory. The Chinese Coast Guard's patrols and law enforcement in the relevant waters, safeguarding the sea and protecting the borders, are legitimate and reasonable, providing no opportunity for anyone coveting Chinese territory. There is no need for relevant parties to be alarmed. We urge Japan to exercise caution in its words and actions and refrain from any actions that could escalate the situation; otherwise, it will only shoot itself in the foot.”
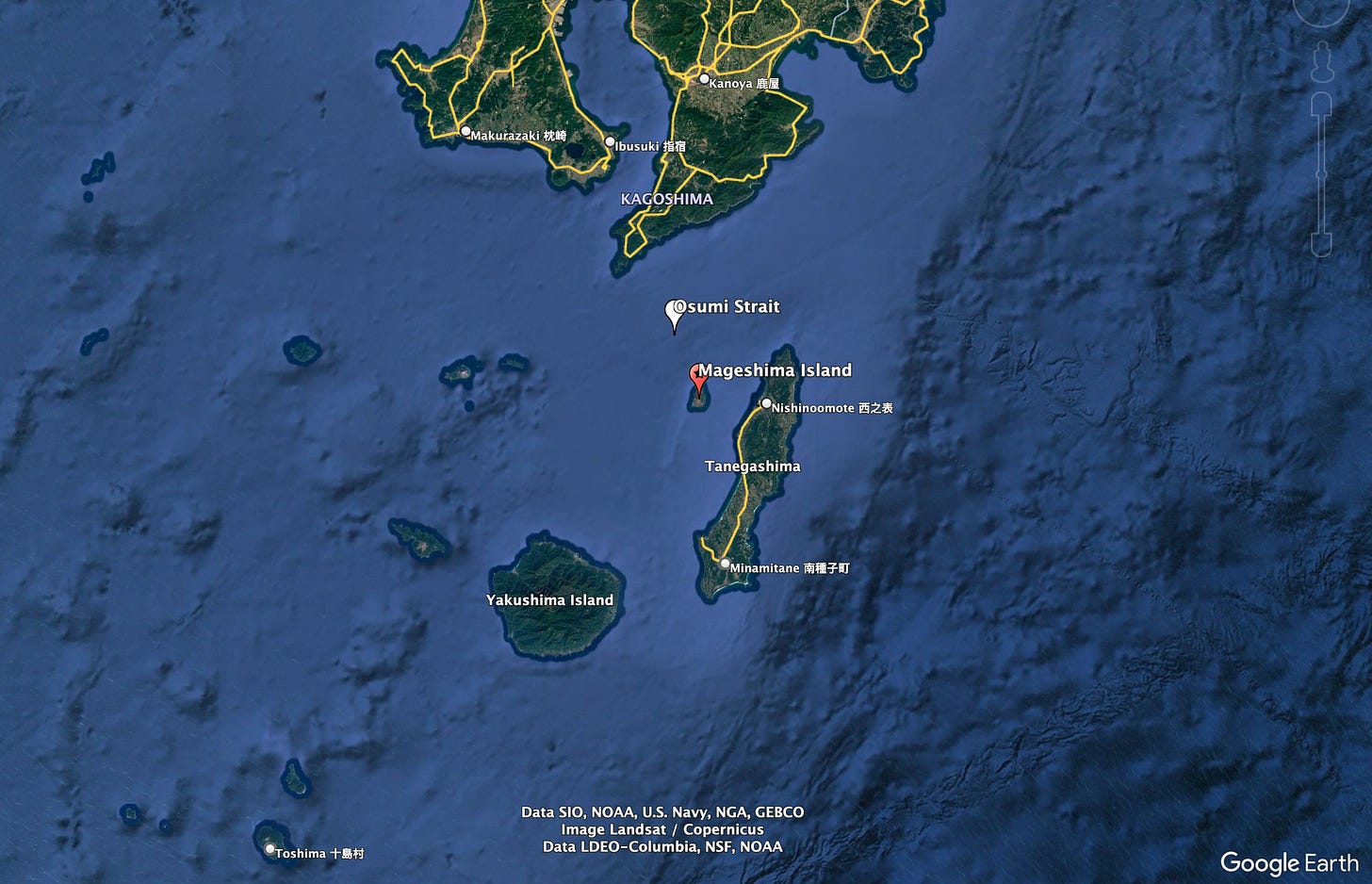
China Conducted Record Number of Transits Through Strategic Osumi Strait
Chinese warships conducted a record 15 passages through the Osumi Strait, one of the waterways separating the Japanese mainland from its southern islands. The increased number of transits may coincide with the ongoing development of a new joint US-Japan military base on Mageshima island located on the southern side of the strait.
Takeaways:
China claims its export controls strictly target companies involved in the Japanese defense industry. However, it often interprets dual-use technology very broadly, and the uncertainty created by Beijing's export control regime is likely part of its strategy to pressure Japanese leaders into retreating from its assertive stance on Taiwan.
2025 was an especially active year for the Chinese naval forces, with unprecedented naval campaigns and new warships. Heightened tensions with Japan will likely increase the operational tempo of China’s navy and coast guard further in 2026. Clashes between Japanese mariners and the China Coast Guard and maritime militia are possible but armed conflict between the Japanese and Chinese navies remain highly unlikely.
3. IRANIAN REGIME SCRAMBLING FOR STRATEGY TO HALT PROTESTS
Iranian Protests Intensifying at Two Week Mark
Saturday January 10 marked the fourteenth day of mass anti-government protests in Iran. According to Human Rights Activists in Iran (HRAI), the protests have spread to over 574 locations in 96 cities. The government’s subsequent crackdown has led to a total of 116 deaths and 2,638 arrests.
Protesters confront Iranian security forces in Kerman on January 10. Source: IranWire (@Farsi_Iranwire) on Telegram
Iranian protesters chant pro-monarchy slogans in Ponak, Tehran on January 10. Source: IranWire (@Farsi_Iranwire) on Telegram
Iran Reportedly Recruiting Iraqi Militias to Help Break up Protests
Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps is recruiting Iraqi Shiite militias to help crack down on protests according to a January 7 report by Iran International.
“According to information received by Iran International, Iranian-backed Iraqi militias began recruiting fighters four days ago to help the Islamic Republic’s forces suppress protests in Iran.
“So far, around 800 Iraqi Shiite militiamen have been deployed, almost all of them members of Kataib Hezbollah, Harakat al-Nujaba, Sayyid al-Shuhada and the Badr Organization.
“The information indicates that Iraqi government officials are aware of the mobilization of forces to assist Tehran. The transfer of these fighters is said to be taking place through the Shalamcheh, Chazabeh and Khosravi border crossings, under the cover of ‘pilgrimage trips to the holy shrine of Imam Reza in Mashhad.’”
“In practice, the forces reportedly gather at a base linked to Khamenei base [sic] in Ahvaz before being dispatched to various regions to take part in the violent crackdown on demonstrations.”
Iran Offering $7 Per Month Subsidy to Ease National Economic Woes
This week the Iranian government announced plans to give every Iranian a monthly stipend of one million tomans (approximately $7) to alleviate the impact of the deterioration of the country’s currency, a key driver of the current protests.
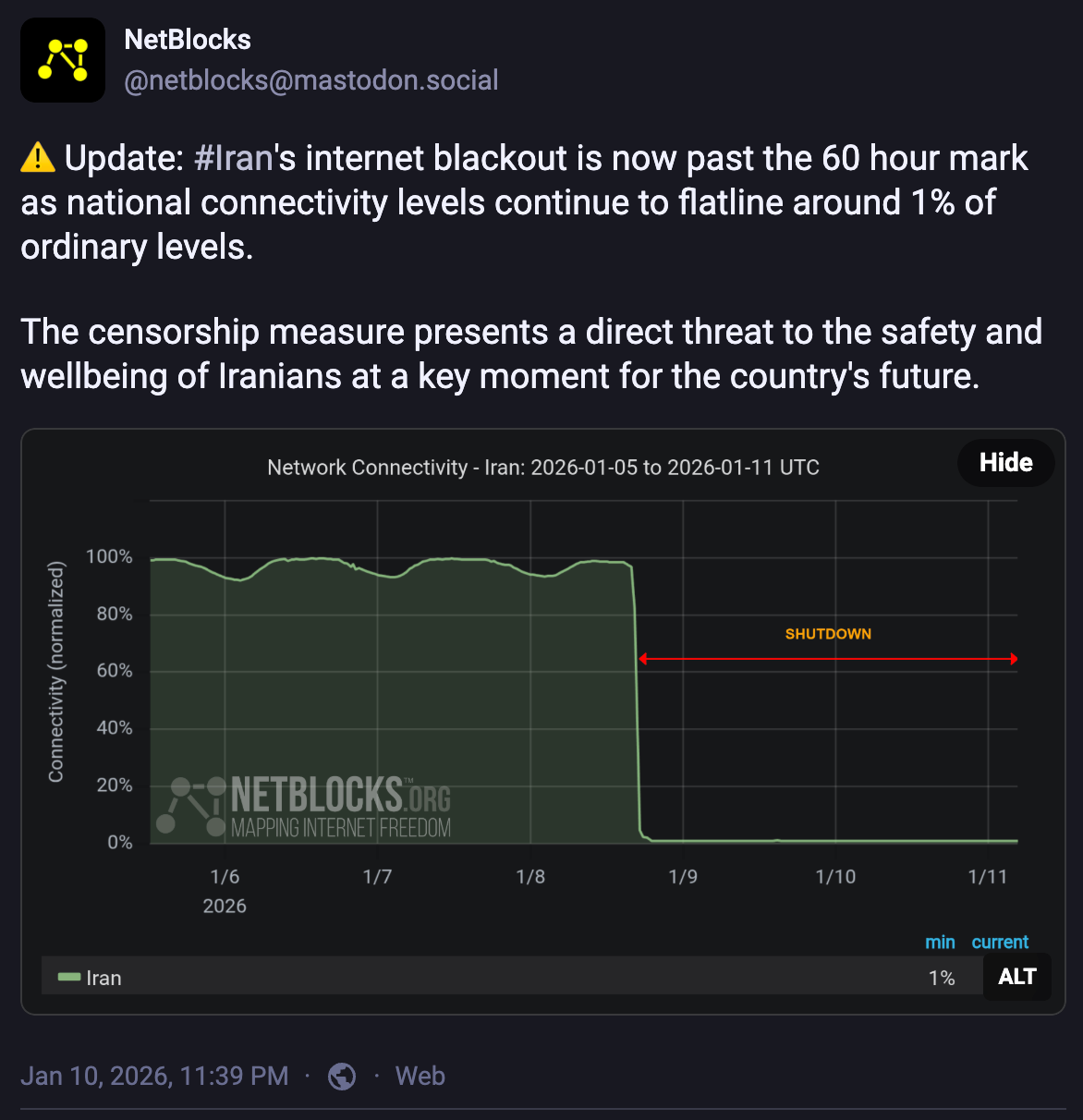
Iran Restricts Internet and Cell Service in Response to Protests
This week Iranian authorities imposed sweeping cuts in internet connectivity and cellular service in response to growing protests. The internet cuts appear to have been introduced on January 8 according to internet freedom monitor Netblocks. While Iran has previously introduced national communications blackouts, some experts consider the current shutdown to be the most sophisticated and restrictive to date.
Takeaways:
Protests have significantly intensified in their second week. As noted in the Weekly Significant Activity Report - January 3, 2026 which covered the first week of protests:
“According to leading independent Iranian human rights group, Human Rights Activists in Iran (HRAI), the protests have spread to over 174 locations in 60 cities across Iran since beginning on December 28. At least 15 protesters and one member of Iran’s security forces have been killed in the unrest, and over 582 people have been arrested.”
By comparison the second week of protests featured seven times as many deaths and five times as many arrests.
Despite employing various tactics, Iran's primary strategy for ending the protests has been violence. Authorities are likely to escalate repression in the coming week with attacks on demonstrators and increased executions, under the cover of the current communications blackout. The Center for Human Rights in Iran notes that Iranian authorities killed over 1,000 protesters following internet restrictions imposed during the wave of anti-government protests in 2019. Fear of mass killings has been heightened after Iran’s Attorney General Mohammad Movahedi Azad warned on January 10 that protesters were “waging war against God,” a crime punishable by death.
There has been mixed reporting that Iranian authorities have been able to block Starlink. According to IranWire, the regime has employed jammers capable of blocking Starlink internet connections, but the effectiveness of the jamming likely varies by region, giving some users better connectivity than others.
Numerous US publications such as the Wall Street Journal have suggested that the Iranian people have heeded calls by the US-exiled Iranian Prince Reza Pahlavi to show up and protest. While there are many Iranians who would welcome the return of the Iranian monarchy, and there have been pro-Shah chants observed during the protests, it’s not clear that Pahlavi has played a major role in either motivating or organizing the current protests. The call Pahlavi made for national protests at 8pm on January 8 and 9 coincided with days of already intensifying demonstrations, suggesting the prince astutely inserted himself into the events rather than instigated them.
Background on Reza Pahlavi’s involvement in the current protests. Source: CNN on YouTube
4. IRAN CONDUCTS NAVAL DRILLS WITH RUSSIA, CHINA AND SOUTH AFRICA
This week the Iranian navy joined the navies of Russia, China, and South Africa for “Will for Peace 2026” exercises in Simon’s Town South Africa. The event features ships and military observers from the BRICS Plus grouping and will run from January 9-16, 2026. The theme for the exercise is “Joint Actions to Ensure the Safety of Shipping and Maritime Economic Activities.”
Iran’s newly commissioned Sahand destroyer and Kordestan floating base appear in videos of the exercise. A Chinese destroyer and replenishment ship and a Russian corvette are also taking part in the exercises.
Chinese, Russian, and Iranian Warships in Simon’s Town, South Africa. Source: SA Defence News
Takeaways:
This event, anticipated in Weekly Significant Activity Report - December 27, 2025, was planned as a BRICS Plus event long before the current wave of protests broke out and therefore does not represent a new show of military support for Iran by Russia and China. In fact a press release from China’s Ministry of Defense for the event notably omits any mention of the Iranian Navy participating in the drills.
“In early to mid-January, the “Peace Will-2026” joint maritime exercise will be held in the airspace and waters near Simonstown, South Africa, with participation from BRICS member countries including China, Russia, and South Africa. The exercise’s theme is “Joint Actions to Safeguard Important Shipping Routes and Economic Activities,” and it will include drills on counter-terrorism rescue and maritime strike operations, as well as professional technical exchanges and ship visits. The exercise aims to further deepen military exchanges and cooperation among participating countries and enhance their joint ability to respond to maritime threats.”
5. NORTH KOREA TESTS POSSIBLE HYPERSONIC MISSILES
On January 4, North Korea launched two ballistic missiles into the Sea of Japan. According to the Japanese Ministry of Defense, the missiles exhibited unusual flight characteristics:
“Both ballistic missiles may have flown on an irregular trajectory, and the analysis is ongoing. The first one was fired at around 7:54 a.m., had a maximum altitude of approximately 50 kilometers and a flight distance of approximately 900 kilometers. The second one was fired at around 8:05 a.m. and had a maximum altitude of approximately 50 kilometers and a flight distance of approximately 950 kilometers.”
North Korea has claimed the test involved “hypersonic missiles”, a possible explanation for the irregular flight trajectories.
Takeaways:
The test likely involved a Hwasong-11E short-range ballistic missile launcher, as each launcher contains two missiles (the same number fired on January 4) equipped with hypersonic glide vehicles.

While North Korea conducts frequent tests to advance the development of its ballistic missiles, it often does so in response to undesirable geopolitical events. Two events likely prompted this test: the US’s capture of Venezuelan President Nicolas Maduro on January 3, and the beginning of South Korean President Lee Jae Myung’s state visit to China on January 4.